PHP Form Validation
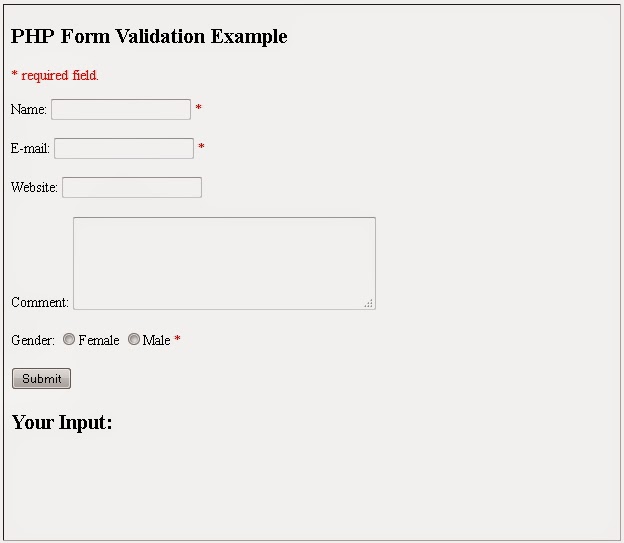
The HTML form we will be working at in these chapters, contains various input fields: required and optional text fields, radio buttons, and a submit button:Think SECURITY when processing PHP forms! These pages will show how to process PHP forms with security in mind. Proper validation of form data is important to protect your form from hackers and spammers!
| Field | Validation Rules |
|---|---|
| Name | Required. + Must only contain letters and whitespace |
| Required. + Must contain a valid email address (with @ and .) | |
| Website | Optional. If present, it must contain a valid URL |
| Comment | Optional. Multi-line input field (textarea) |
| Gender | Required. Must select one |
Text Fields
The name, email, and website fields are text input elements, and the comment field is a textarea. The HTML code looks like this:
Name: <input type="text" name="name">
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email">
Website: <input type="text" name="website">
Comment: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email">
Website: <input type="text" name="website">
Comment: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea>
Radio Buttons
The gender fields are radio buttons and the HTML code looks like this:
Gender:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male
The Form Element
The HTML code of the form looks like this:
<form method="post" action="<?php echo
htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
What is the $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] variable?
The $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] is a super global variable that returns the filename of the currently executing script.
What is the htmlspecialchars() function?
The htmlspecialchars() function converts special characters to HTML entities. This means that it will replace HTML characters like < and > with < and >. This prevents attackers from exploiting the code by injecting HTML or Javascript code (Cross-site Scripting attacks) in forms.
Big Note on PHP Form Security
The $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] variable can be used by hackers!If PHP_SELF is used in your page then a user can enter a slash (/) and then some Cross Site Scripting (XSS) commands to execute.
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of computer security vulnerability typically found in Web applications. XSS enables attackers to inject client-side script into Web pages viewed by other users.
<form method="post" action="<?php echo $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"];?>">
<form method="post" action="test_form.php">
However, consider that a user enters the following URL in the address bar:
http://www.example.com/test_form.php/%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ealert('hacked')%3C/script%3E
<form method="post" action="test_form.php/"><script>alert('hacked')</script>
Be aware of that any JavaScript code can be added inside the <script> tag! A hacker can redirect the user to a file on another server, and that file can hold malicious code that can alter the global variables or submit the form to another address to save the user data, for example.
How To Avoid $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] Exploits?
$_SERVER["PHP_SELF"] exploits can be avoided by using the htmlspecialchars() function.The form code should look like this:
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
<form method="post" action="test_form.php/"><script>alert('hacked')</script>">
Validate Form Data With PHP
The first thing we will do is to pass all variables through PHP's htmlspecialchars() function.When we use the htmlspecialchars() function; then if a user tries to submit the following in a text field:
<script>location.href('http://www.hacked.com')</script>
- this would not be executed, because it would be saved as HTML escaped code, like this:
<script>location.href('http://www.hacked.com')</script>
The code is now safe to be displayed on a page or inside an e-mail.
We will also do two more things when the user submits the form:
- Strip unnecessary characters (extra space, tab, newline) from the user input data (with the PHP trim() function)
- Remove backslashes (\) from the user input data (with the PHP stripslashes() function)
We will name the function test_input().
Now, we can check each $_POST variable with the test_input() function, and the script looks like this:
Example
<?php
// define variables and set to empty values
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
function test_input($data) {
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
// define variables and set to empty values
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = $website = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
$website = test_input($_POST["website"]);
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
function test_input($data) {
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
However, in the example above, all input fields are optional. The script works fine even if the user does not enter any data.
The next step is to make input fields required and create error messages if needed.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar